- 322 BC : Chandragupta Maurya founds the Mauryan Empire by overthrowing the Nanda Dynasty.
- 317–316 BC : Chandragupta Maurya conquers the Northwest of the Indian subcontinent.
- 305–303 BC : Chandragupta Maurya gains territory from the Seleucid Empire.
- 298–269 BC : Reign of Bindusara, Chandragupta's son. He conquers parts of Deccan, southern India.
- 269–232 BC : The Mauryan Empire reaches its height under Ashoka, Chandragupta's grandson.
- 261 BC : Ashoka conquers the kingdom of Kalinga.
- 250 BC : Ashoka builds Buddhist stupas and erects pillars bearing inscriptions.
- 184 BC : The empire collapses when Brihadnatha, the last emperor, is killed by Pushyamitra Shunga, a Mauryan general and the founder of the Shunga Empire.
The Maurya Empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya, with help from Chanakya, a Brahmin teacher at Takshashila. According to several legends, Chanakya traveled to Magadha, a kingdom that was large and militarily powerful and feared by its neighbors, but was insulted by its king Dhana Nanda, of the Nanda Dynasty. Chanakya swore revenge and vowed to destroy the Nanda Empire.[14] Meanwhile, the conquering armies of Alexander the Great refused to cross the Beas River and advance further eastward, deterred by the prospect of battling Magadha. Alexander returned to Babylon and re-deployed most of his troops west of the Indus river. Soon after Alexander died in Babylon in 323 BCE, his empire fragmented, and local kings declared their independence, leaving several smaller disunited satraps.
The Greek generals Eudemus, and Peithon,
ruled until around 317 BCE, when Chandragupta Maurya (with the help of
Chanakya, who was now his advisor) utterly defeated the Macedonians and
consolidated the region under the control of his new seat of power in
Magadha.
Chandragupta Maurya's rise to power is shrouded in mystery and
controversy. On one hand, a number of ancient Indian accounts, such as
the drama Mudrarakshasa (Poem of Rakshasa – Rakshasa
was the prime minister of Magadha) by Visakhadatta, describe his royal
ancestry and even link him with the Nanda family. A kshatriya clan known as the Maurya's are referred to in the earliest Buddhist texts, Mahaparinibbana Sutta.
However, any conclusions are hard to make without further historical
evidence. Chandragupta first emerges in Greek accounts as
"Sandrokottos". As a young man he is said to have met Alexander. He is also said to have met the Nanda king, angered him, and made a narrow escape.
Chanakya's original intentions were to train a guerilla army under
Chandragupta's command. The Mudrarakshasa of Visakhadutta as well as the
Jaina work Parisishtaparvan talk of Chandragupta's alliance with the
Himalayan king Parvatka, sometimes identified with Porus (Sir John
Marshall "Taxila", p18, and al.)
Chanakya encouraged Chandragupta Maurya and his army to take over the
throne of Magadha. Using his intelligence network, Chandragupta
gathered many young men from across Magadha and other provinces, men
upset over the corrupt and oppressive rule of king Dhana, plus the
resources necessary for his army to fight a long series of battles.
These men included the former general of Taxila, accomplished students
of Chanakya, the representative of King Porus of Kakayee, his son
Malayketu, and the rulers of small states.
Preparing to invade Pataliputra, Maurya came up with a strategy. A
battle was announced and the Magadhan army was drawn from the city to a
distant battlefield to engage Maurya's forces. Maurya's general and
spies meanwhile bribed the corrupt general of Nanda. He also managed to
create an atmosphere of civil war in the kingdom, which culminated in
the death of the heir to the throne. Chanakya managed to win over
popular sentiment. Ultimately Nanda resigned, handing power to
Chandragupta, and went into exile and was never heard of again. Chanakya
contacted the prime minister, Rakshasas, and made him understand that
his loyalty was to Magadha, not to the Nanda dynasty, insisting that he
continue in office. Chanakya also reiterated that choosing to resist
would start a war that would severely affect Magadha and destroy the
city. Rakshasa accepted Chanakya's reasoning, and Chandragupta Maurya
was legitimately installed as the new King of Magadha. Rakshasa became
Chandragupta's chief advisor, and Chanakya assumed the position of an
elder statesman.
-
The approximate extent of the Magadha state in the 5th century BCE.
-
The Nanda Empire at its greatest extent under Dhana Nanda c. 323 BCE.
-
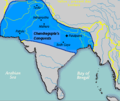
The Maurya Empire when it was first founded by Chandragupta Maurya c. 320 BCE, after conquering the Nanda Empire when he was only about 20 years old.
-
Chandragupta Maurya later extended the borders of the empire southward into the Deccan Plateau c. 300 BCE.[21]
-
Ashoka the Great extended into Kalinga during the Kalinga War c. 265 BCE, and established superiority over the southern kingdoms.
Chandragupta Maurya
Main article: Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta campaigned against the Macedonians when Seleucus I Nicator, in the process of creating the Seleucid Empire
out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great, tried to reconquer
the northwestern parts of India in 305 BCE. Seleucus failed (Seleucid–Mauryan war), the two rulers finally concluded a peace treaty: a marital treaty (Epigamia)
was concluded, in which the Greeks offered their Princess for alliance
and help from him. Chandragupta snatched the satrapies of Paropamisade (Kamboja and Gandhara), Arachosia (Kandhahar) and Gedrosia (Balochistan), and Seleucus I received 500 war elephants that were to have a decisive role in his victory against western Hellenistic kings at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BCE. Diplomatic relations were established and several Greeks, such as the historian Megasthenes, Deimakos and Dionysius resided at the Mauryan court.
Chandragupta established a strong centralized state with an administration at Pataliputra, which, according to Megasthenes, was "surrounded by a wooden wall pierced by 64 gates and 570 towers— (and) rivaled the splendors of contemporaneous Persian sites such as Susa and Ecbatana." Chandragupta's son Bindusara extended the rule of the Mauryan empire towards southern India. The famous Tamil poet Mamulanar of the Sangam literature described how the Deccan Plateau was invaded by the Maurya army. He also had a Greek ambassador at his court, named Deimachus Strabo.
Megasthenes describes a disciplined multitude under Chandragupta, who live simply, honestly, and do not know writing:
- "The Indians all live frugally, especially when in camp. They dislike a great undisciplined multitude, and consequently they observe good order. Theft is of very rare occurrence. Megasthenes says that those who were in the camp of Sandrakottos, wherein lay 400,000 men, found that the thefts reported on any one day did not exceed the value of two hundred drachmae, and this among a people who have no written laws, but are ignorant of writing, and must therefore in all the business of life trust to memory. They live, nevertheless, happily enough, being simple in their manners and frugal. They never drink wine except at sacrifices. Their beverage is a liquor composed from rice instead of barley,
Bindusara was the son of the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya and his queen Durdhara. During his reign, the empire expanded southwards. According to the Rajavalikatha a Jain work, the original name of this emperor was Simhasena. According to a legend mentioned in the Jain texts, Chandragupta's Guru and advisor Chanakya used to feed the emperor with small doses of poison to build his immunity against possible poisoning attempts by the enemies.[23] One day, Chandragupta not knowing about poison, shared his food with his pregnant wife queen Durdhara who was 7 days away from
delivery. The queen not immune to the poison collapsed and died within
few minutes. Chanakya entered the room the very time she collapsed, and
in order to save the child in the womb, he immediately cut open the dead
queen's belly and took the baby out, by that time a drop of poison had
already reached the baby and touched its head due to which child got a
permanent blueish spot (a "bindu") on his forehead. Thus, the newborn
was named "Bindusara".
Bindusara, just 22 year-old, inherited a large empire that consisted of what is now, Northern, Central and Eastern parts of India along with parts of Afghanistan and Baluchistan. Bindusara extended this empire to the southern part of India, as far as what is now known as Karnataka.
He brought sixteen states under the Mauryan Empire and thus conquered
almost all of the Indian peninsula (he is said to have conquered the
'land between the two seas' – the peninsular region between the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea). Bindusara didn't conquer the friendly Dravidian kingdoms of the Cholas, ruled by King Ilamcetcenni, the Pandyas, and Cheras. Apart from these southern states, Kalinga
(modern Odisha) was the only kingdom in India that didn't form the part
of Bindusara's empire. It was later conquered by his son Ashoka, who served as the viceroy of Ujjaini during his father's reign.
Bindusara's life has not been documented as well as that of his
father Chandragupta or of his son Ashoka. Chanakya continued to serve as
prime minister during his reign. According to the medieval Tibetan
scholar Taranatha who visited India, Chanakya helped Bindusara "to
destroy the nobles and kings of the sixteen kingdoms and thus to become
absolute master of the territory between the eastern and western
oceans." During his rule, the citizens of Taxila revolted twice. The reason for the first revolt was the maladministration of Suseema,
his eldest son. The reason for the second revolt is unknown, but
Bindusara could not suppress it in his lifetime. It was crushed by
Ashoka after Bindusara's death.
Ambassadors from the Seleucid Empire (such as Deimachus) and Egypt visited his courts. He maintained good relations with the Hellenic World.
Unlike his father Chandragupta (who at a later stage converted to Jainism), Bindusara believed in the Ajivika sect. Bindusara's guru Pingalavatsa (alias Janasana) was a Brahmin of the Ajivika sect. Bindusara's wife, Queen Subhadrangi (alias Queen Aggamahesi) was a Brahmin
also of the Ajivika sect from Champa (present Bhagalpur district).
Bindusara is accredited with giving several grants to Brahmin
monasteries (Brahmana-bhatto).
Bindusara died in 272 BCE (some records say 268 BCE) and was succeeded by his son Ashoka the Great.
Ashoka the Great
Aśoka pillar at Sarnath
ca.250 BCE.
ca.250 BCE.
Chandragupta's grandson Ashoka Vardhana Maurya, son of Bindusara, was
also known as Asoka, Ashoka or Ashoka The Great. (reign 272- 232 BCE)
As a young prince, Ashoka was a brilliant commander who crushed
revolts in Ujjain and Taxila. As monarch he was ambitious and
aggressive, re-asserting the Empire's superiority in southern and
western India. But it was his conquest of Kalinga
(262–261 BCE) which proved to be the pivotal event of his life.
Although Ashoka's army succeeded in overwhelming Kalinga forces of royal
soldiers and civilian units, an estimated 100,000 soldiers and
civilians were killed in the furious warfare, including over 10,000 of
Ashoka's own men. Hundreds of thousands of people were adversely
affected by the destruction and fallout of war. When he personally
witnessed the devastation, Ashoka began feeling remorse. Although the
annexation of Kalinga was completed, Ashoka embraced the teachings of Buddhism, and renounced war and violence. He sent out missionaries to travel around Asia and spread Buddhism to other countries.
Ashoka implemented principles of ahimsa
by banning hunting and violent sports activity and ending indentured
and forced labor (many thousands of people in war-ravaged Kalinga had
been forced into hard labor and servitude). While he maintained a large
and powerful army, to keep the peace and maintain authority, Ashoka
expanded friendly relations with states across Asia and Europe, and he
sponsored Buddhist missions. He undertook a massive public works
building campaign across the country. Over 40 years of peace, harmony
and prosperity made Ashoka one of the most successful and famous
monarchs in Indian history. He remains an idealized figure of
inspiration in modern India.
Ashoka pillar at Vaishali
The Edicts of Ashoka, set in stone, are found throughout the Subcontinent. Ranging from as far west as Afghanistan and as far south as Andhra (Nellore District),
Ashoka's edicts state his policies and accomplishments. Although
predominantly written in Prakrit, two of them were written in Greek, and one in both Greek and Aramaic. Ashoka's edicts refer to the Greeks, Kambojas, and Gandharas
as peoples forming a frontier region of his empire. They also attest to
Ashoka's having sent envoys to the Greek rulers in the West as far as
the Mediterranean. The edicts precisely name each of the rulers of the Hellenic world at the time such as Amtiyoko (Antiochus), Tulamaya (Ptolemy), Amtikini (Antigonos), Maka (Magas) and Alikasudaro (Alexander)
as recipients of Ashoka's proselytism. The Edicts also accurately
locate their territory "600 yojanas away" (a yojanas being about
7 miles), corresponding to the distance between the center of India and
Greece (roughly 4,000 miles).







No comments:
Post a Comment